British Standard Pipe (BSP) identifies specific screw threads. BSP threads are by far the most popular with the United Kingdom, all of Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa adopting these standards. To use BSP screw threads correctly, you must identify the male and female parts. The male thread has an external shape, whereas the female thread has an internal shape.
Types of BSP Threads
There are two types of threads – BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel, which is sometimes referred to as ‘straight’) and BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper).
BSPP – Is a parallel/straight thread with a 55° angle and are not designed to seal. The seal is accomplished with the use of an O-ring, gasket, or bonded washer to create a leak tight closure. This bonded ring seal is sandwiched in-between a shoulder on the male fitting and the face of the female fitting is squeezed in place.
- Thread conforms to ISO 228-1
- Port conforms to ISO 1179
- Pitch & diameter measured in inches e.g. G1/4-19
- Parallel threads require o-ring, crush washer, gasket or metal to metal seal between connections for pressure tight connection
- Thread angle is 55°
BSPT – A British standard taper thread has a 55° angle and has a changing diameter. Tapered threads have ‘peaks and valleys’ or also known as ‘crest and roots’. The surface between the ‘crest and roots’ is called a ‘flank’. It is common to incorrectly identify tapered pipes as NPT ‘National Pipe Thread’ however, NPT pipes have a 60°flank angle. The seal is secured via metal-to-metal wedging.
- Thread conforms to ISO 7
- Pitch and diameter are measured in inches, e.g. R3/8-19
- Tapered thread profile seals by metal to metal interference fit, usually requires sealing compound for pressure tight connection
- Taper angle is 1° 47′, the same as NPT(F)
- Thread angle is 55°
- Not interchangeable with NPT(F)
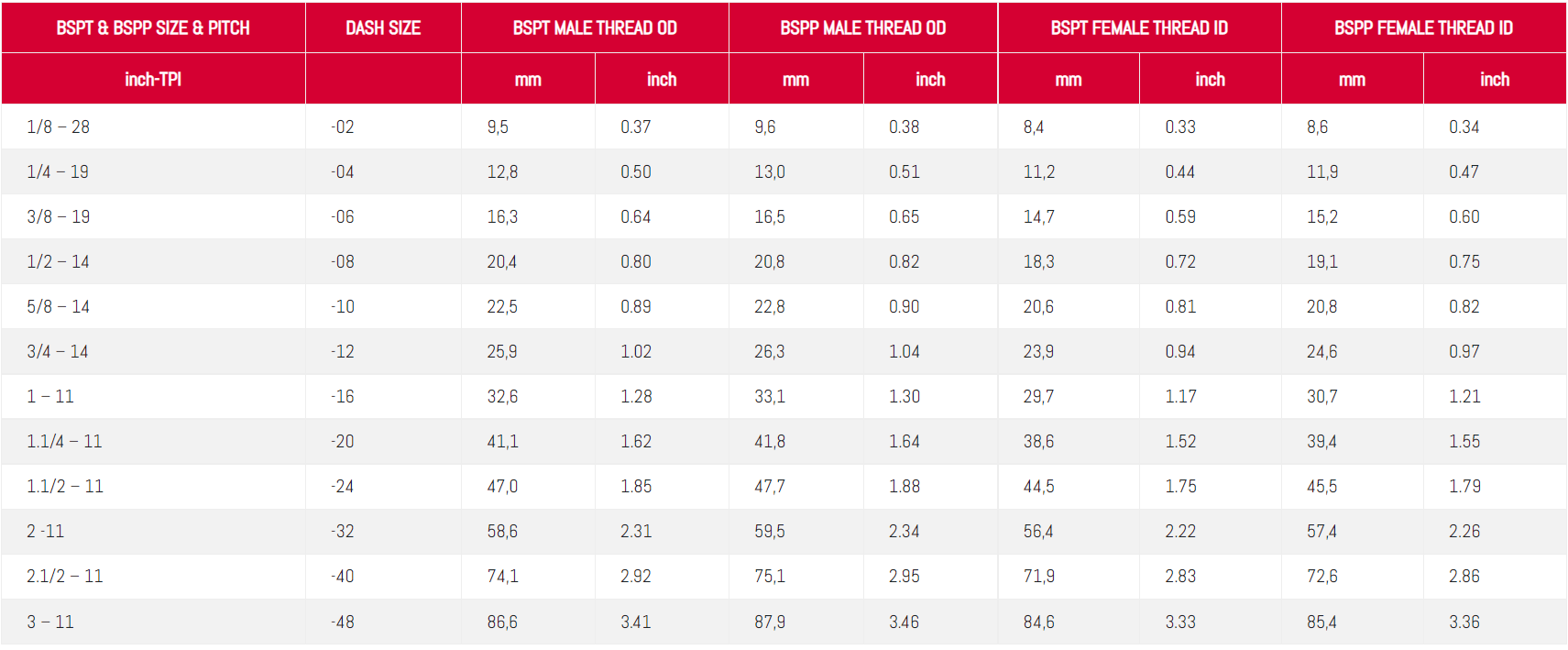
BSPP & BSPT threads dimensions: