DIN-3852-1 is the same as ISO 9974-1. The DIN 3852-1 / ISO 9974-1 port style, on the other hand, has threads coming all the way up to the surface of the port.
The fittings have parallel threads and seal using various sealing rings, washers or metal to metal seals.
The types of sealing styles shown in DIN-3852-1 / ISO 9974 are below:
Type E – For fixed stud ends only. These use a trapezoidal-sectioned elastomeric seal which is embedded into a groove that’s cut into the stud end of the adapter fitting.

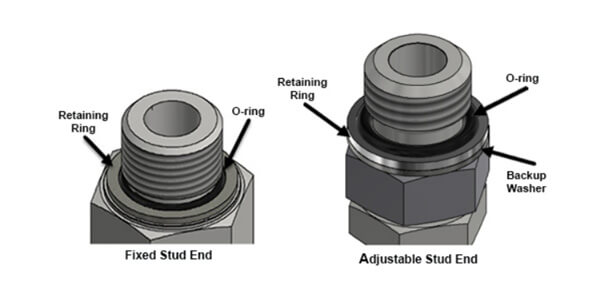
Type G and Type H – utilizes an O-ring and retaining ring for fixed and adjustable stud ends.
Type D – Applies to fixed studs only. These styles utilize a seal with an elastomer bonded to the ID of a metal ring.
Type A – Applies to fixed studs only. This style utilizes a soft metal seal, typically made of a soft material such as copper.
Type B – Applies to fixed studs only. This style uses a cutting face seal as a direct metal to metal seal between the adapter fitting and the face of the port. A slight ridge of material on the fitting coins the surface of the port to create the seal.
The most important thing to remember about this style is that it seals on the spotface of the port. The styles with an elastomer seal must have a means of creating a cavity for retaining the seal material so it can seal properly. For example, looking at the O-ring and retaining ring fitting style, a cavity is created by the port, the fitting, and the metal retaining ring. This cavity helps to ensure proper compression of the O-ring, creating a leak-free connection. A common issue for this style is a missing retaining ring – it might have fallen off or wasn’t seen as being necessary. Without the retaining ring, the O-ring would be performing like a gasket, and will easily be pushed out when the system is pressurized and cause a leak.




